Important Elevation and Slope Relationships within Eddy or Backwater Basins
To maximize performance potential of your Eddy or Backwater Basins, design for the following…
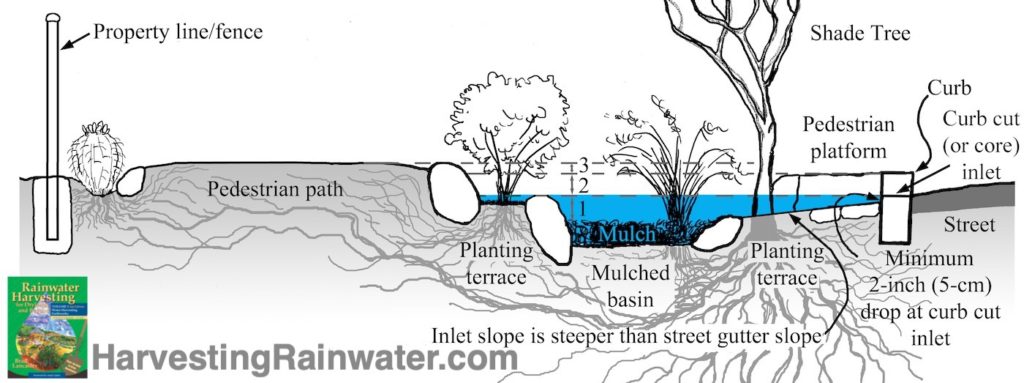
Blue represents stormwater captured from street just after flow has ceased in street gutter.
Note how planting terrace elevation should be below street gutter/inlet elevation, so terrace will be fully watered in a runoff event.
Illustration: Joe Marshall
The following is based on tip 9 (Three Key Elevation Relationships of Water-Harvesting Earthworks) from chapter one of Rainwater Harvesting for Drylands and Beyond, Volume 2, by Brad Lancaster.
Elevation 1: Bottom of basin, and the top of the mulch within it, is lower than the elevation of the curb-cut inlet so the structure accepts and holds street runoff. The deeper the basin in relation to its overflow, the greater its water-holding capacity.
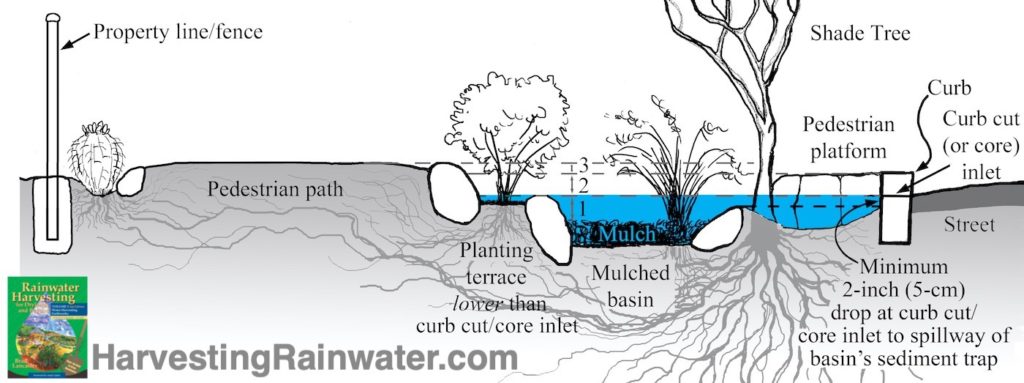
Sediment trap spillway must be at least 2-inches (5-cm) lower that the inlet elevation.
Nothing is planted in sediment trap, nor is it rocked; so it is easy to dig out accumulated sediment as needed.
Elevation 2: Curb-cut inlet is the low point of the basin’s perimeter, so water will overflow at (or back up to) the inlet and the pavement-stabilized street-curb gutter. Planting terraces are typically the same elevation as the curb-cut inlet (and higher than the bottom of basin), so plants less water-tolerant than those in bottom of basins will thrive—allowing for a greater diversity of plantings. Terraces also reduce the otherwise-sudden drop a basin would represent along adjoining paths and pedestrian platforms.
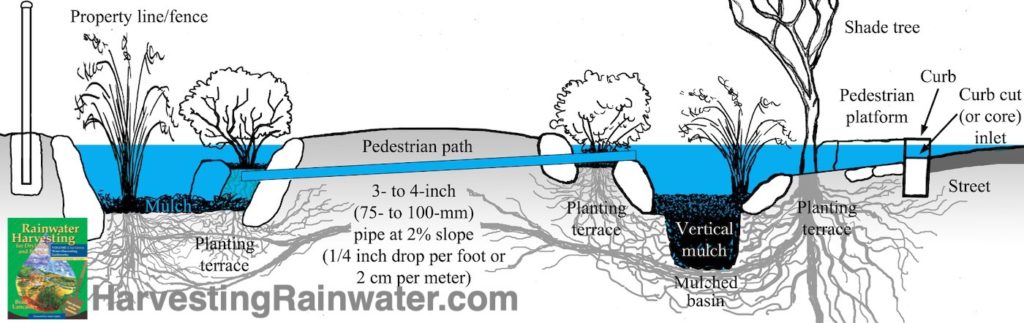
Street-side basin capacity has also been increased with vertical mulch – see Volume 2 book for more.
This example also shows a wider public right-of-way, and one way to get water from the street-side basin to the property-side basin without flowing over the pedestrian path.
Illustration: Joe Marshall
Elevation 3: Pathway elevation is level with, or no more than two inches (5 cm) higher than, top of street curb. At the same time, you’ll want ensure the elevation along the entire length of pathway adjoining the basin is at least 4 inches (10 cm) higher than the elevation of the basin’s inlet/overflow. This way water will not flow over path into adjoining properties.
Note: A common mistake to avoid when digging a street-side basin is to spread all the resulting dirt atop the adjoining earthen path to the point of raising the path more than two inches (5 cm) above the street curb. In the past, I and others have been guilty of raising the path 12 inches (30 cm) higher than the street curb. What results is a basin that appears to be very deep (and is perhaps slightly precarious) from the perspective of pedestrians walking atop the excessively raised path. But from the water’s perspective, the basin’s depth and water-harvesting capacity are actually much less than what the pedestrian perceives, since the water depth is not determined by the path elevation, but rather by the relationship between the elevation of the basin’s bottom and the elevation of the basin’s curb-cut inlet/overflow.
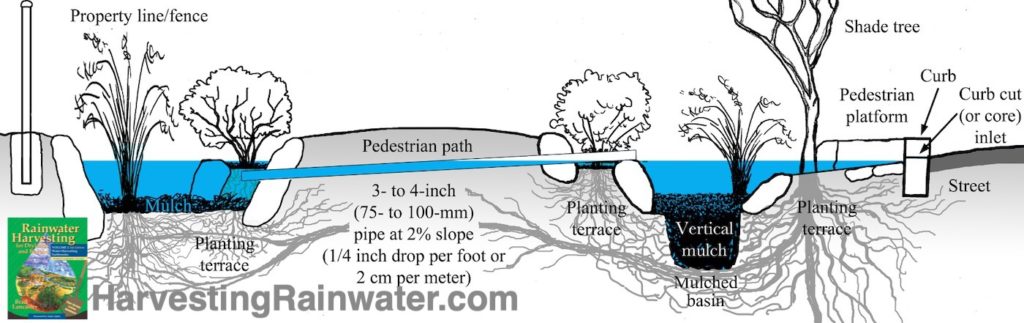
Illustration: Joe Marshall
Important Slope Relationships of a Street-Side Basin with Curb-Cut or Curb-Core Inlet
The following is based on the erosion-triangle pattern presented in appendix 1 of Rainwater Harvesting for Drylands and Beyond, Volume 1, 2nd Edition:
- Maintain a minimum 2-inch (5-cm) drop at inlet (see fig.1)
- Inlet slope is steeper than street-curb-gutter slope (see fig. 1)
Both of the slope relationships above will speed up, rather than slow, the flow of incoming water so sediment in street runoff won’t drop out of flow and clog inlet.
Note: Inlet slope can be stabilized with only one layer of rock. Rock more than one course high/deep is a waste of material and may impede germination of beneficial vegetation between rocks. Top of all rock must be below the elevation of the inlet.
For more information
Such as how to increase the capacity of these basins, construction & planting guides, how to calculate capacity & costs, and examples (most of the info on this page came from Volume 2)—buy, read, and share these award-winning books:

Volume 1

Volume 2
For more on curb cuts and curb cores, visit this section. For more on how to choose the right plant for the right place within or beside the basin—Rain Garden Planting Zones—see here.
